Description
Cura Heat Back And Shoulder Pain Heat Patch, 7 Patches
Cura Heat Back And Shoulder Pain Heat Patch provide 12 hours of active heat therapy. Once removed the pain relief can continue for a further 12 hours resulting in up to 24 hours pain relief. Simply open the sachet and apply to clothing/ underwear where the heat radiates through to the source of pain – decreasing stiffness, improving mobility and relaxing tense aching muscles. Non-medicinal, fragrance free and with a thin discreet design, Cura-Heat provides a convenient way to manage your back and shoulder pain.
Cura Heat Back and Shoulder Pain are small discreet rectangular heat packs that provide targeted, temporary 24 hour warming relief from minor muscular and joint aches and pains.
Just open the Cura Heat sachet and apply to clothing or underwear where the heat radiates through to the source of pain, increasing circulation, decreasing stiffness and relaxing sore muscles.
The Cura Heat Back and Shoulder Pain patch is fragrance free, non-medicinal and with a thin discreet design, they are ideal to use anywhere.
This product should not be applied directly to the skin.
Cura Heat Back and Shoulder Pain warms up gradually and reaches maximum heat within approximately 30 minutes. Cura-Heat Back and Shoulder Pain is air-activated.
Benefits:
- Long-lasting. Up to 24 Hours of pain relief
- Air-activated heat patch for targeted warming relief from back and shoulder pain
- Non-medicinal and Ready to use
- Can be used with medicine
- It increases blood circulation and relieves sore and stiff muscles
Why do Heat Patches relieve pain in my Back And Shoulder?
Cura-Heat Neck & Shoulder Heat Packs provide heat therapy for sore and aching muscles. The pads are self-heating and will heat up within just 5 minutes, radiating heat through your muscles and helping to decrease stiffness, relax sore muscles, and relieve your pain.
Heat patches dilate blood vessels, promoting blood flow and helping to relax painful muscles. Tissue injury activates nerve endings in the skin called nociceptors, which transmit signals to the brain to inform it of pain.
At the same time, neurotransmitters initiate a reflex that causes muscles to contract at the injury site, often to the point of spasm. Fortunately, heat can activate temperature-sensitive thermoreceptors, which initiate nerve signals to block those from nociceptors
Reference: Science focus
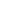 +44 (0) 1375 846 316
+44 (0) 1375 846 316




Reviews
There are no reviews yet